Abstract
Case Report
Challenges in the diagnosis and management of severe Pneumocystis jirovecii pneumonia in a non-HIV-infected patient - A case report
Mark Taubert, Lorenz Weidhase, Sirak Petros and Henrik Rueffert*
Published: 17 October, 2018 | Volume 3 - Issue 1 | Pages: 023-026
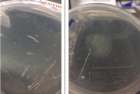
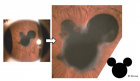
A 64-year-old woman was referred to our hospital due to progressive dypnoea for the past week, combined with fever and type 1 respiratory failure. White blood cell count and procalcitonin level were normal. The Chest X-ray showed bilateral disseminated pulmonary infiltrates. Within the next 24 hours the patient developed a severe ARDS. A first diagnostic work-up for typical and atypical pathogens as well as serological tests for CMV, RSV, HIV and HSV were negative. Analysis of a second bronchoalveolar lavage fluid revealed Pneumocystis jiroveci DNA. The patient was successfully treated with trimethoprim-sulfamethoxazole and off label use with caspofungin. The cause of the infection was a six week treatment with dexamethasone. The patient developed a toxic epidermal necrolysis during further course, but completely recovered.
Pneumonia with Pneumocystis jirovecii must also be taken into account in non-HIV patients, whenever there are any indications that cellular immunity may be depressed.
Read Full Article HTML DOI: 10.29328/journal.jcicm.1001015 Cite this Article Read Full Article PDF
References
- Mansharamani NG, Garland R, Delaney D, Koziel H. Management and outcome patterns for adult Pneumocystis carinii pneumonia, 1985 to 1995: comparison of HIV-associated cases to other immunocompromised states. Chest. 2000; 118: 704-711. Ref.: https://goo.gl/EPe8B7
- Bellani G, Laffey JG, Pham T, Fan E, Brochard L, et al. Epidemiology, Patterns of Care, and Mortality for Patients With Acute Respiratory Distress Syndrome in Intensive Care Units in 50 Countries. JAMA. 2016; 315: 788-800. Ref.: https://goo.gl/LMG3Dv
- Lobo ML,Esteves F, de Sousa B, Cardoso F, Cushion MT, et al. Therapeutic Potential of Caspofungin Combined with Trimethoprim-Sulfamethoxazole for Pneumocystis Pneumonia: A Pilot Study in Mice. PLoS One., 2013; 8: e70619. Ref.: https://goo.gl/N9annU
- Sekula P, Dunant A, Mockenhaupt M, Naldi L, Bouwes Bavinck JN, et al. Comprehensive survival analysis of a cohort of patients with Stevens-Johnson syndrome and toxic epidermal necrolysis. J. Invest. Dermatol. 2013; 133: 1197-204. Ref.: https://goo.gl/JRc6T8
- Li H, Huang H, He H. Successful treatment of severe Pneumocystis pneumonia in an immunosuppressed patient using caspofungin combined with clindamycin: a case report and literature review. BMC. Pulm. Med. 2016; 16: 144. Ref.: https://goo.gl/wuvPtt
Figures:
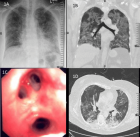
Figure 1
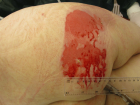
Figure 2
Similar Articles
-
Phenibut Overdose in Combination with Fasoracetam: Emerging Drugs of AbuseCristian Merchan*,Ryan Morgan,John Papadopoulos,David Fridman. Phenibut Overdose in Combination with Fasoracetam: Emerging Drugs of Abuse. . 2016 doi: 10.29328/journal.jcicm.1001001; 1: 001-004
-
Nursing Care of ICU Patients Lightly Sedated with DexmedetomidineÅsa Engström*,Maria Johansson,Mia Mattsson,Ulrica Strömbäck. Nursing Care of ICU Patients Lightly Sedated with Dexmedetomidine. . 2016 doi: 10.29328/journal.jcicm.1001002; 1: 005-013
-
Complicated Hepatitis A Virus Infection: A Report of Three Cases from Single Tertiary Referral CenterOmkolsoum M Alhaddad,Maha M Elsabaawy*,Khalid A Gameel,Marwa Elfauomy,Olfat Hendy,Eman A Rewisha. Complicated Hepatitis A Virus Infection: A Report of Three Cases from Single Tertiary Referral Center. . 2016 doi: 10.29328/journal.jcicm.1001003; 1: 014-020
-
Critical Management of Status EpilepticusFarahnaz Fallahian*,Seyed MohammadReza Hashemian*. Critical Management of Status Epilepticus. . 2017 doi: 10.29328/journal.jcicm.1001004; 2: 001-015
-
Comparative Hemodynamic Evaluation of the LUCAS® Device and Manual Chest Compression in Patients with Out-of-Hospital Cardiac ArrestMirek S,Opprecht N*,Daisey A,Milojevitch E,Soudry- Faure A,Freysz M. Comparative Hemodynamic Evaluation of the LUCAS® Device and Manual Chest Compression in Patients with Out-of-Hospital Cardiac Arrest. . 2017 doi: 10.29328/journal.jcicm.1001005; 2: 016-024
-
Chemotherapy Exposure and outcomes of Chronic Lymphoid Leukemia PatientsJosephina G Kuiper*,Patience Musingarimi,Christoph Tapprich,Fernie JA Penning-van Beest,Maren Gaudig. Chemotherapy Exposure and outcomes of Chronic Lymphoid Leukemia Patients. . 2017 doi: 10.29328/journal.jcicm.1001006; 2: 025-033
-
Knowledge, attitude and practices associated with diagnosis and management of Skin and Soft Tissue Infections (SSTIs) among Pediatric Residents and Physicians in a Tertiary Hospital in United Arab Emirates (UAE)Eiman Al Blooshi,Farah Othman,Abeer Al Naqbi,Majid Al Rumaithi,Khawla Fikry,Mariam Al Jneibi,Hossam Al Tatari*. Knowledge, attitude and practices associated with diagnosis and management of Skin and Soft Tissue Infections (SSTIs) among Pediatric Residents and Physicians in a Tertiary Hospital in United Arab Emirates (UAE) . . 2017 doi: 10.29328/journal.jcicm.1001007; 2: 034-039
-
Unusual presentation of a bilateral basilar stroke: BradycardiaZidouh S*,Jidane S,Nabhani T,Chouaib N,Sirbou R,Belkouch,Belyamani L. Unusual presentation of a bilateral basilar stroke: Bradycardia. . 2017 doi: 10.29328/journal.jcicm.1001008; 2: 040-041
-
Sinking Skin Flap SyndromeLiew BS*,Rosman AK,Adnan JS. Sinking Skin Flap Syndrome. . 2017 doi: 10.29328/journal.jcicm.1001009; 2: 042-048
-
Intensive Care Units (ICU): The clinical pharmacist role to improve clinical outcomes and reduce mortality rate- An undeniable functionLuisetto M*,Ghulam Rasool Mashori. Intensive Care Units (ICU): The clinical pharmacist role to improve clinical outcomes and reduce mortality rate- An undeniable function. . 2017 doi: 10.29328/journal.jcicm.1001010; 2: 049-056
Recently Viewed
-
Septic Shock on Bartholinitis: Case Report and Modern Surgical ApproachesOumaima Fakir*,Hanaa Lazhar,Aziz Slaoui,Amina Lakhdar,Aziz Baydada. Septic Shock on Bartholinitis: Case Report and Modern Surgical Approaches. Clin J Obstet Gynecol. 2025: doi: 10.29328/journal.cjog.1001183; 8: 015-018
-
Forensic Comparison of Textile Fibre for Identification using X-ray Diffraction TechniqueMC Janaki*,S Anil Kumar. Forensic Comparison of Textile Fibre for Identification using X-ray Diffraction Technique. J Forensic Sci Res. 2023: doi: 10.29328/journal.jfsr.1001055; 7: 083-088
-
Forensic Insights into Multiple Stab Wounds: Autopsy Findings from a Case of Sixty Stab WoundsAsif Hussain*. Forensic Insights into Multiple Stab Wounds: Autopsy Findings from a Case of Sixty Stab Wounds. J Forensic Sci Res. 2025: doi: 10.29328/journal.jfsr.1001075; 9: 021-024
-
Sinonasal Myxoma Extending into the Orbit in a 4-Year Old: A Case PresentationJulian A Purrinos*, Ramzi Younis. Sinonasal Myxoma Extending into the Orbit in a 4-Year Old: A Case Presentation. Arch Case Rep. 2024: doi: 10.29328/journal.acr.1001099; 8: 075-077
-
The relationship between IT consumption and anxiety in Pakistani youthWaqar Husain*,Sehrish Mobeen. The relationship between IT consumption and anxiety in Pakistani youth. Arch Psychiatr Ment Health. 2020: doi: 10.29328/journal.apmh.1001026; 4: 084-086
Most Viewed
-
Evaluation of Biostimulants Based on Recovered Protein Hydrolysates from Animal By-products as Plant Growth EnhancersH Pérez-Aguilar*, M Lacruz-Asaro, F Arán-Ais. Evaluation of Biostimulants Based on Recovered Protein Hydrolysates from Animal By-products as Plant Growth Enhancers. J Plant Sci Phytopathol. 2023 doi: 10.29328/journal.jpsp.1001104; 7: 042-047
-
Sinonasal Myxoma Extending into the Orbit in a 4-Year Old: A Case PresentationJulian A Purrinos*, Ramzi Younis. Sinonasal Myxoma Extending into the Orbit in a 4-Year Old: A Case Presentation. Arch Case Rep. 2024 doi: 10.29328/journal.acr.1001099; 8: 075-077
-
Feasibility study of magnetic sensing for detecting single-neuron action potentialsDenis Tonini,Kai Wu,Renata Saha,Jian-Ping Wang*. Feasibility study of magnetic sensing for detecting single-neuron action potentials. Ann Biomed Sci Eng. 2022 doi: 10.29328/journal.abse.1001018; 6: 019-029
-
Pediatric Dysgerminoma: Unveiling a Rare Ovarian TumorFaten Limaiem*, Khalil Saffar, Ahmed Halouani. Pediatric Dysgerminoma: Unveiling a Rare Ovarian Tumor. Arch Case Rep. 2024 doi: 10.29328/journal.acr.1001087; 8: 010-013
-
Physical activity can change the physiological and psychological circumstances during COVID-19 pandemic: A narrative reviewKhashayar Maroufi*. Physical activity can change the physiological and psychological circumstances during COVID-19 pandemic: A narrative review. J Sports Med Ther. 2021 doi: 10.29328/journal.jsmt.1001051; 6: 001-007

HSPI: We're glad you're here. Please click "create a new Query" if you are a new visitor to our website and need further information from us.
If you are already a member of our network and need to keep track of any developments regarding a question you have already submitted, click "take me to my Query."