Abstract
Research Article
Evaluation of unexplained clinical features of hepatic diseases through biopsies among hospitalized children: A cross-sectional study in Lahore, Pakistan
Ibtasam Ahmad, Muhammad Haris, Amnah Javed and Muhammad Azhar*
Published: 11 September, 2018 | Volume 3 - Issue 1 | Pages: 013-019
Objectives: There are variations in therapeutic regimens of different liver diseases. The accurate diagnosis ensures prompt recovery from these diseases. The present study aimed to evaluate the underlying causes of unexplained signs and symptoms associated with liver diseases through biopsies.
Methods: A retrospective study was conducted in a public child care specialty of Lahore, Pakistan. The data was collected from medical records of the patients who were index hospitalized with unexplained clinical presentation of liver disease between 1st July, 2017 and 31st December, 2017. Data were analyzed by using Statistical Packages for Social Sciences (IBM SPSS Statistics for Windows, Version 21.0. Armonk, NY: IBM Corp.), and Microsoft Excel (MS Office 2010).
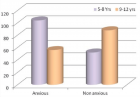
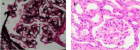
Results: Overall, the records of 53 patients were selected for the study. Most of them were 11 to 15 years of age. The patients were presented with unexplained hepatomegaly (60.4%) and jaundice (40.7%) during index hospitalization which made them eligible for liver biopsy (LB). The findings of LB revealed that the underlying causes of liver diseases in most of the cases were metabolic (33.9%) and inflammatory disorders (22.6%). Majority of the patients were ≤4 years of age, however cryptogenic cirrhosis (39.1%) was commonly found in >10 years of age. Although most of the patients were suffering from metabolic disorders (p-value=0.07) and liver cirrhosis (p-value=0.08) but these were not statistically significant.
Conclusions: LB was beneficial in evaluating the etiologies of unexplained signs and symptoms of liver diseases. It was found that glycogen storage diseases and liver cirrhosis were the most common etiologies of liver diseases among pediatric patients. But etiologies like metabolic and inflammatory diseases were insignificantly associated with gender.
Read Full Article HTML DOI: 10.29328/journal.jcicm.1001013 Cite this Article Read Full Article PDF
Keywords:
Liver; Inflammatory disorder; Metabolic disorder; Biopsy; Etiology; Cirrhosis
References
- Litten JB, Tomlinson GE. Liver tumors in children. The oncologist. 2008; 13: 812-820. Ref.: https://goo.gl/Ggavf6
- Dezsőfi A, Baumann U, Dhawan A, Durmaz O, Fischler B, et al. Liver biopsy in children: position paper of the ESPGHAN Hepatology Committee. J Pediatr Gastroenterol Nutr. 2015; 60: 408-420. Ref.: https://goo.gl/hfNmfj
- Mehnaz A, Billo AG, Zuberi SJ. Liver disorders in children. Journal of Pakistan Medical Association. 1990; 40: 62-64. Ref.: https://goo.gl/Rbcqze
- Dehghani SN, Haghighat M, Imanieh MH, Geramizadeh B, Eskandari Z, et al. Percutaneous Needle Biopsy in the diagnosis of liver diseases in children. Journal of Comprehensive Pediatrics, 2013; 4: 184-188. Ref.: https://goo.gl/br2ug7
- Bezerra JA, Balistreri WF. Cholestatic syndromes of infancy and childhood. Semin Gastrointest Dis. 2001; 12: 54-65. Ref.: https://goo.gl/5xmfBP
- Dehghani SM, Haghighat M, Imanieh MH, Geramizadeh B. Comparison of different diagnostic methods in infants with cholestasis. World J Gastroenterol. 2006; 12: 5893-5896. Ref.: https://goo.gl/zRpnf6
- Ovchinsky N1, Moreira RK, Lefkowitch JH, Lavine JE. The liver biopsy in modern clinical practice: a pediatric point-of-view. Adv Anat Pathol. 2012; 19: 250-262. https://goo.gl/Q6s4wh
- Alswat KA, Mumtaz K, Jafri W. Liver biopsy for histological assessment: the case in favor. Saudi journal of gastroenterology: official journal of the Saudi Gastroenterology Association. 2010; 16: 133-139. Ref.: https://goo.gl/RUo5ZW
- Dezsőfi A, Knisely AS. Liver biopsy in children 2014: Who, whom, what, when, where, why? Clin Res Hepatol Gastroenterol. 2014; 38: 395-398. Ref.: https://goo.gl/xorJ5H
- Van Ha TG. Liver biopsy in liver transplant recipients. in Seminars in interventional radiology. 2004. Copyright© 2004 by Thieme Medical Publishers, Inc., 333 Seventh Avenue, New York, NY 10001, USA. Ref.: https://goo.gl/eBJFp8
- Czaja AJ, Carpenter HA. Optimizing diagnosis from the medical liver biopsy. Clin Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2007; 5: 898-907. Ref.: https://goo.gl/GWc3hN
- Karim AB, Rahman MM. Safety of blind liver biopsy. The Indian Journal of Pediatrics. 2004; 71: 899-901. Ref.: https://goo.gl/ASauEH
- Govender P, Jonas MM, Alomari AI, Padua HM, Dillon BJ, et al. Sonography-guided percutaneous liver biopsies in children. American Journal of Roentgenology. 2013; 201: 645-650. Ref.: https://goo.gl/B1zG2B
- Ahmad M, Afzal S, Roshan E, Mubarik A, Bano S, et al. Usefulness of needle biopsy in the diagnosis of pediatric liver disorders. J Pak Med Assoc. 2005; 55: 24-28. Ref.: https://goo.gl/xBPLmD
- >Cheema H, Parkash A, Suleman H, Fayyaz Z. Safety of Outpatient Blind Percutaneous Liver Biopsy (OBPLB) in Children and to Document the Spectrum of Pediatric Liver Disease. Pak Pediatr J. 2015; 39: 12-18. Ref.: https://goo.gl/9whfEQ
- Roy A, Samanta T, Purkait R, Mukherji A, Ganguly S. Etiology, clinical spectrum and outcome of metabolic liver diseases in children. J Coll Physicians Surg Pak. 2013; 23: 194-198. Ref.: https://goo.gl/7cnRej
- Anwar C, Khalilullah. A histological study of clinically unexplained hepatomegaly in children. Pak J Pathol. 1990; 1: 79-82.
- Monajemzadeh M, Tabriz HM, Mahjoub F, Fallahi G, Farahmand F. Liver needle biopsy in Iraninan pediatric patients: diagnostic significance and pattern of liver diseases. Indian J Pathol Microbiol. 2009; 52: 10-13. Ref.: https://goo.gl/Hw8E2t
- Zhang HF, Yang XJ, Zhu SS, Zhao JM, Zhang TH, et al. Pathological changes and clinical manifestations of 1020 children with liver diseases confirmed by biopsy. Hepatobiliary Pancreat Dis Int. 2004. 3: 395-398. Ref.: https://goo.gl/ahpCdP
- Obafunwa J, Elesha S. Childhood liver diseases in Jos, Nigeria: a retrospective histopathological study. East Afr Med J. 1991; 68: 702-706. Ref.: https://goo.gl/G2ai5z
- Ullah F, Khan S, Afridi AK, Rahman SU. Frequency of different causes of cirrhosis liver in local population. Gomal Journal of Medical Sciences. 2012; 10. Ref.: https://goo.gl/zMF8ws
- Ahmed T. Evaluation of liver biopsy in undiagnosed cases of liver enlargement. Pak Paedtr J. 1988; 3: 171-175.
- Shakoor K. Histological diagnosis of paediatric liver diseases. Pak Paediatr J. 1987; 2: 73-80.
- Dhole SD, Kher AS, Ghildiyal RG, Tambse MP. Chronic Liver Diseases in Children: Clinical profile and Histology. J Clin Diagn Res. 2015; 9: SC04-07. Ref.: https://goo.gl/iwS2KE
- Scorza M, Elce A, Zarrilli F, Liguori R, Amato F, et al. Genetic diseases that predispose to early liver cirrhosis. Int J Hepatol. 2014; 2014. 713754. Ref.: https://goo.gl/unvH2Q
Similar Articles
-
Knowledge, attitude and practices associated with diagnosis and management of Skin and Soft Tissue Infections (SSTIs) among Pediatric Residents and Physicians in a Tertiary Hospital in United Arab Emirates (UAE)Eiman Al Blooshi,Farah Othman,Abeer Al Naqbi,Majid Al Rumaithi,Khawla Fikry,Mariam Al Jneibi,Hossam Al Tatari*. Knowledge, attitude and practices associated with diagnosis and management of Skin and Soft Tissue Infections (SSTIs) among Pediatric Residents and Physicians in a Tertiary Hospital in United Arab Emirates (UAE) . . 2017 doi: 10.29328/journal.jcicm.1001007; 2: 034-039
-
Evaluation of Desmin, α-SMA and hTERT expression in pulmonary fibrosis and lung cancerFarahnaz Fallahian*,Seyed Ali Javad Moosavi,Frouzandeh Mahjoubi,Samira Shabani,Pegah Babaheidarian,Tayebeh Majidzadeh. Evaluation of Desmin, α-SMA and hTERT expression in pulmonary fibrosis and lung cancer. . 2018 doi: 10.29328/journal.jcicm.1001011; 3: 001-009
-
Evaluation of unexplained clinical features of hepatic diseases through biopsies among hospitalized children: A cross-sectional study in Lahore, PakistanIbtasam Ahmad,Muhammad Haris,Amnah Javed,Muhammad Azhar*. Evaluation of unexplained clinical features of hepatic diseases through biopsies among hospitalized children: A cross-sectional study in Lahore, Pakistan . . 2018 doi: 10.29328/journal.jcicm.1001013; 3: 013-019
-
Novel Complication of Nusinersen Treatment: HyponatremiaYasemin Coban*. Novel Complication of Nusinersen Treatment: Hyponatremia. . 2018 doi: 10.29328/journal.jcicm.1001014; 3: 020-022
-
Acute pneumonia: Facts and realities against etiological hypotheses and beliefsKlepikov Igor*. Acute pneumonia: Facts and realities against etiological hypotheses and beliefs. . 2019 doi: 10.29328/journal.jcicm.1001019; 4: 010-017
-
Do you really want to improve the results of treatment for acute pneumonia?Klepikov Igor*. Do you really want to improve the results of treatment for acute pneumonia?. . 2019 doi: 10.29328/journal.jcicm.1001021; 4: 023-027
-
Levosimendan in sepsisUgur Koca*,Burcu Tanay Demirdöven. Levosimendan in sepsis. . 2020 doi: 10.29328/journal.jcicm.1001030; 5: 020-021
-
Metabolic syndrome: A case reportDragan Klaric,Marta Martinis*,Marta Klaric. Metabolic syndrome: A case report. . 2021 doi: 10.29328/journal.acem.1001022; 5: 031-035
-
Prognosis factors for dengue shock syndrome in childrenEka Fitri Sari Ningrum*. Prognosis factors for dengue shock syndrome in children. . 2021 doi: 10.29328/journal.jcicm.1001039; 6: 033-037
-
Spinal cord involvement in tuberculous meningitis: a case report and brief review of literatureOriba Dan Langoya*,Adrian Mwota Nampogo,Andia Irene. Spinal cord involvement in tuberculous meningitis: a case report and brief review of literature. . 2022 doi: 10.29328/journal.jcicm.1001040; 7: 001-004
Recently Viewed
-
Anesthetic Management of a Patient with Left Ventricular Thrombus Posted for Emergency LaparotomyArpita Das*. Anesthetic Management of a Patient with Left Ventricular Thrombus Posted for Emergency Laparotomy. Int J Clin Anesth Res. 2025: doi: 10.29328/journal.ijcar.1001028; 9: 013-016
-
Satellite-Based Analysis of Air Pollution Trends in Khartoum before and After the ConflictHossam Aldeen Anwer*,Abubakr Hassan,Ghofran Anwer. Satellite-Based Analysis of Air Pollution Trends in Khartoum before and After the Conflict. Ann Civil Environ Eng. 2025: doi: 10.29328/journal.acee.1001074; 9: 001-011
-
Computational Models in Systems and Synthetic Biology: Short OverviewMarian Gheorghe*. Computational Models in Systems and Synthetic Biology: Short Overview. Arch Biotechnol Biomed. 2024: doi: 10.29328/journal.abb.1001037; 8: 001-002
-
Academic Exposure of Doctors-In-Training in Maiduguri, Nigeria: A Five-year Compendium of Residents’ PresentationsYesiru Adeyemi Kareem*, A Shuaib, UB Musami, KU Musa, NM Sani, FM Kadau, PN Ogualili, Kwetishe EE, AA Mshelia. Academic Exposure of Doctors-In-Training in Maiduguri, Nigeria: A Five-year Compendium of Residents’ Presentations. Ann Biomed Sci Eng. 2024: doi: 10.29328/journal.abse.1001027; 8: 001-003
-
Investigate the Effect of Coating Concentration and Coating Thickness on the Anti-microbial Properties of Polycarbonate SheetSaleh Alkarri. Investigate the Effect of Coating Concentration and Coating Thickness on the Anti-microbial Properties of Polycarbonate Sheet. Ann Biomed Sci Eng. 2024: doi: 10.29328/journal.abse.1001029; 8: 011-020
Most Viewed
-
Sinonasal Myxoma Extending into the Orbit in a 4-Year Old: A Case PresentationJulian A Purrinos*, Ramzi Younis. Sinonasal Myxoma Extending into the Orbit in a 4-Year Old: A Case Presentation. Arch Case Rep. 2024 doi: 10.29328/journal.acr.1001099; 8: 075-077
-
Evaluation of Biostimulants Based on Recovered Protein Hydrolysates from Animal By-products as Plant Growth EnhancersH Pérez-Aguilar*, M Lacruz-Asaro, F Arán-Ais. Evaluation of Biostimulants Based on Recovered Protein Hydrolysates from Animal By-products as Plant Growth Enhancers. J Plant Sci Phytopathol. 2023 doi: 10.29328/journal.jpsp.1001104; 7: 042-047
-
Feasibility study of magnetic sensing for detecting single-neuron action potentialsDenis Tonini,Kai Wu,Renata Saha,Jian-Ping Wang*. Feasibility study of magnetic sensing for detecting single-neuron action potentials. Ann Biomed Sci Eng. 2022 doi: 10.29328/journal.abse.1001018; 6: 019-029
-
Physical activity can change the physiological and psychological circumstances during COVID-19 pandemic: A narrative reviewKhashayar Maroufi*. Physical activity can change the physiological and psychological circumstances during COVID-19 pandemic: A narrative review. J Sports Med Ther. 2021 doi: 10.29328/journal.jsmt.1001051; 6: 001-007
-
Pediatric Dysgerminoma: Unveiling a Rare Ovarian TumorFaten Limaiem*, Khalil Saffar, Ahmed Halouani. Pediatric Dysgerminoma: Unveiling a Rare Ovarian Tumor. Arch Case Rep. 2024 doi: 10.29328/journal.acr.1001087; 8: 010-013

HSPI: We're glad you're here. Please click "create a new Query" if you are a new visitor to our website and need further information from us.
If you are already a member of our network and need to keep track of any developments regarding a question you have already submitted, click "take me to my Query."